You may have seen some information in the news about NFTs. Better known as Non-fungible tokens, NFTs are essentially digital art sold and bought on the blockchain. Digital art is artistic work that makes use of digital technologies to create the work, whether in part or wholly. Any digital asset can be an NFT.

In this post, we share with you all you need to know about Non-fungible Tokens (NFTs).
This guide to NFTs is divided into 5 sections.
- Introduction to NFTs
- How NFTs are made and sold
- The benefits of NFTs
- The problems with NFTs
- The future of NFTs.
Introduction to NFTs
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are the hottest addition to the world of cryptocurrency. You may be wondering what they are and whether you should consider making an investment in them.
NFTs are digital files that are hosted on a blockchain ledger. NFTs occur in various forms of digital art such as video games, physical objects, tweets, GIFs or even photographs. Most NFTs are supported on the Ethereum blockchain. There are several platforms available that transform your digital works of art and other multimedia into NFTs that can be traded on the blockchain.
Setting New Records
A lot of interest has risen around NFTs after Mike Winkelmann’s NFT artwork titled ‘The First 500 Days sold for $69 million. Winkelmann’s sale set the record for the highest valued NFT.
Unlike Bitcoin which can be traded for other bitcoins, NFTs are non-fungible. This means that each NFT is unique, sort of in the same way an autograph is unique. They cannot be interchanged with other people’s NFT assets because their underlying value is based on their originality and uniqueness, not related to other NFTs in the system. Each NFT has an authenticity certificate that verifies the originality of a Non-Fungible token.

How NFTs are Made
NFTs run on the Ethereum blockchain. Ethereum works just like other cryptocurrencies. To mine and get rewarded with cryptocurrency, computer algorithms solve cryptographic problems and puzzles and are then ‘rewarded’ with cryptocurrency.
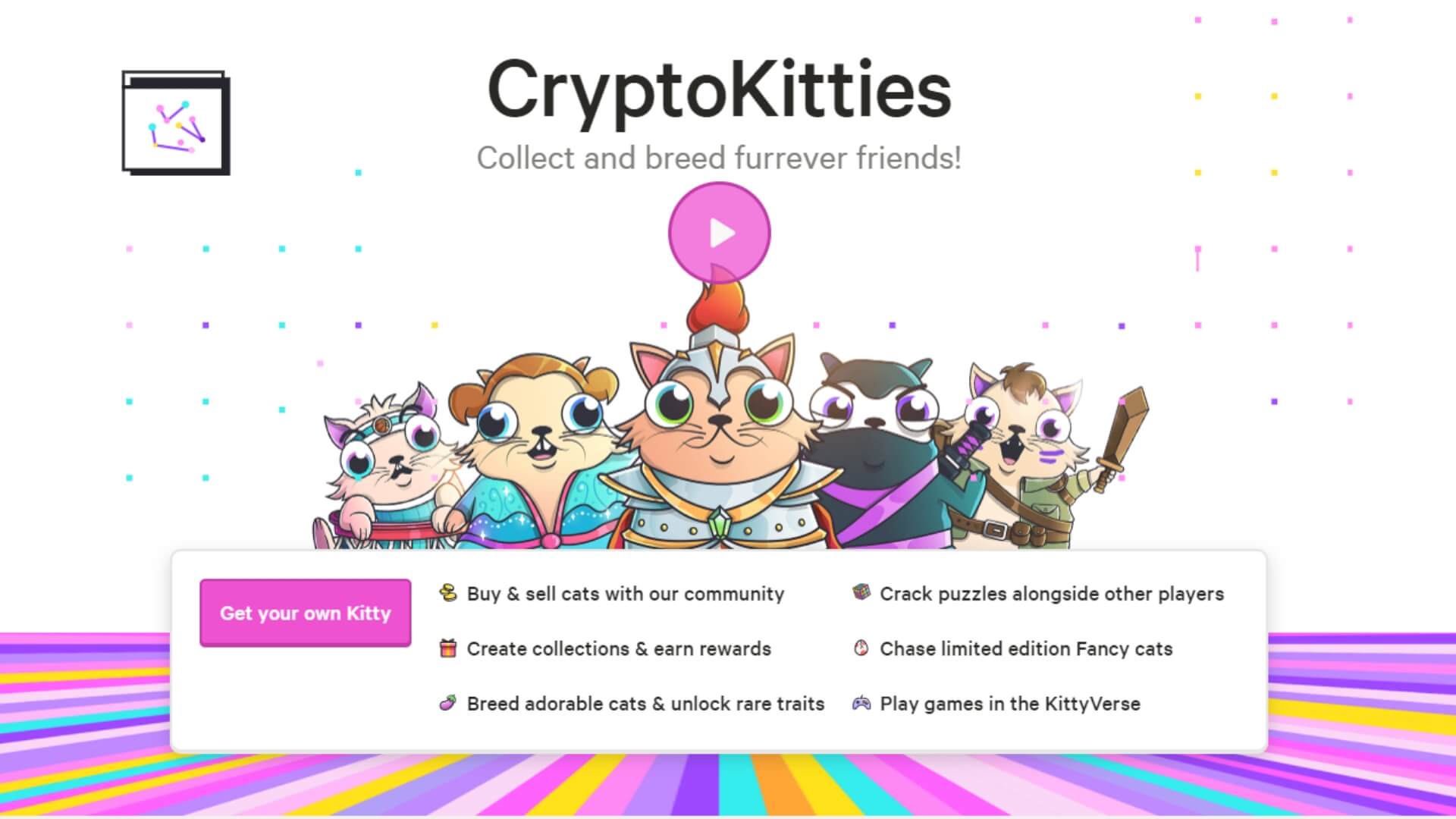
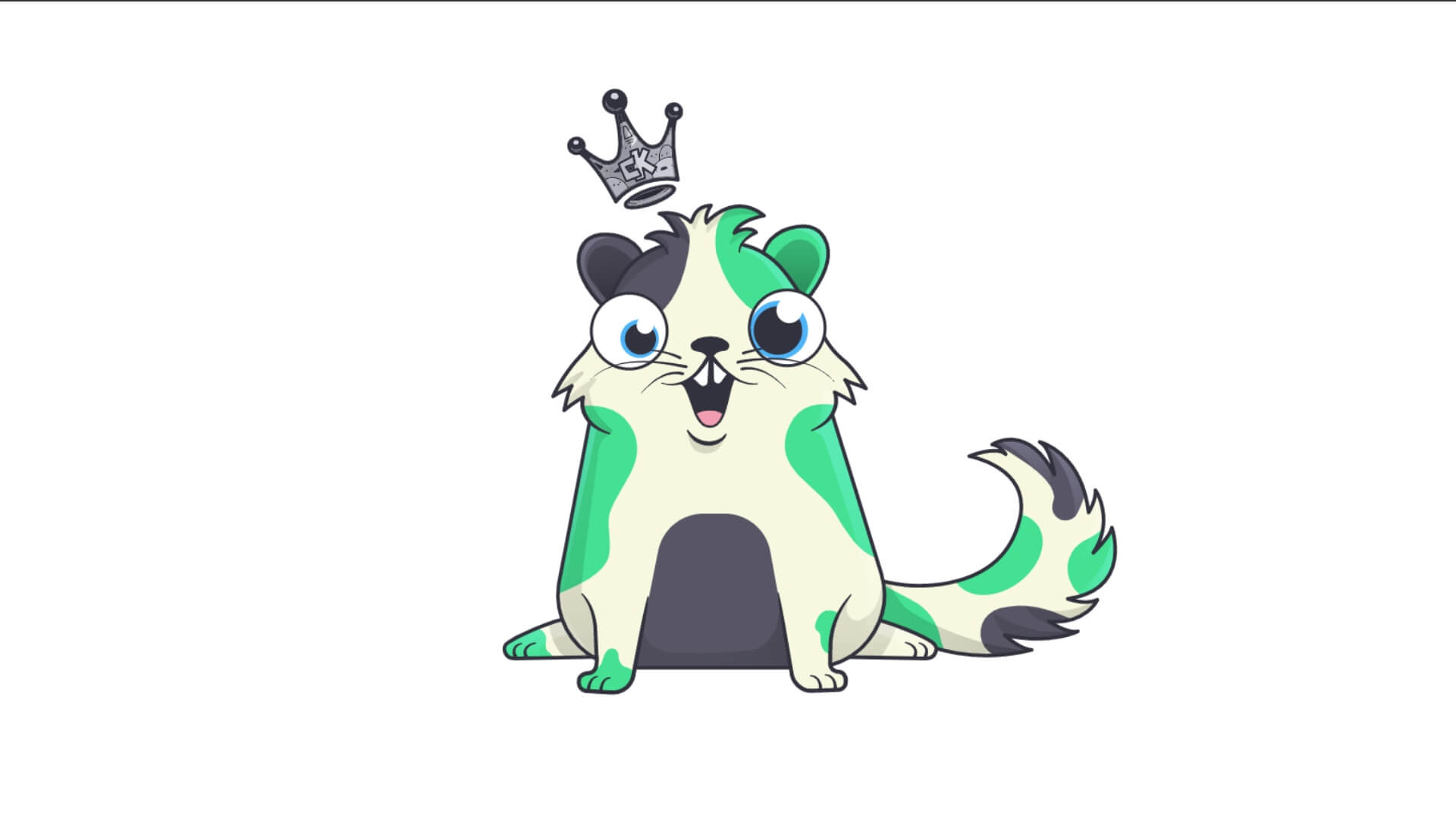
CryptoKitties, one of the world’s first blockchain games, offers ‘CryptoKitties’. These are NFT digital kitties which are one-of-a-kind and 100% owned by the user. The kitties cannot be replicated, taken away, or destroyed.
How to Create NFTs
NFTs be created by anyone with a digital wallet. The digital wallet allows you to receive payment and make payments for NFTs. With a cryptocurrency wallet, you can then connect it to an NFT marketplace of your choice where your digital art can be uploaded. The uploaded digital art content is then transformed into an NFT or Crypto art, ready to be sold globally. NFTs are sold on digital marketplaces where price varies from one platform to another. Some of the platforms where people can buy and sell NFTs are Rarible and OpenSea.
The Benefits of NFTs
One of the main benefits of the NFTs is that authentication of digital art is done using blockchain technology. Blockchain cannot be hacked or manipulated, thus ensuring the uniqueness of a Non-fungible token. For art collectors, this is an important benefit that allows them to authenticate their art and maintain or appreciate their arts’ value.
NFTs have also provided a great avenue for artists and creatives, who for a long time have been underpaid. They allow artists to create their own artwork, determine the price and keep the profits. NFTs are also unique due to the distinguishing information they contain to identify them. Each NFT can be traced to the original issuer.

The Problems with NFTs
Non-fungible tokens are unlimited in supply. By nature of their being digital assets, they can be replicated infinitely. The cost of creating NFTs is nearly zero and with many artists with their own artwork they’d want to trade as NFTs, supply overwhelms demand. This does not sound like a problem until you realize that due to more NFTs of the same artwork existing, demand can be easily met hence a lot of value is lost. In economic terms, the more of something there is in a market, the less the price of the commodity.
NFTs are also run on the Ethereum blockchain, which is mined using powerful and multiple computers that solve cryptographic problems. These computers not only use a lot of electricity to perform the tasks required to mine cryptocurrencies. In one case, an artist who created an NFT artwork ended up using 2 years of electricity in less than a week to create his artwork.

The carbon footprint imposed by NFTs is immense, leading many people to question the sustainability of such an activity in a world that is moving to carbon-neutral or carbon negative forms of economic activity.
The Future of NFTs
There is no doubt that the application of digital assets and the use of technologies such as the blockchain has improved many people’s lives. Nike, the sportswear brand, recently got a patent for blockchain compatible sneakers called ‘CryptoKicks. Nike aims to link cryptographic digital assets with physical products like shoes.
For NFTs to become part of the future, the carbon footprint imposed on the planet needs to be mitigated. One way to reduce the carbon footprint that comes with NFTs is by artists choosing to spend some of their income from the sale of NFTs to support companies and programs that reduce the carbon footprint.

Another way to make NFTs future-proof is to shift the mining of Ethereum and other blockchain assets to use renewable energy sources. If Ethereum is mined using solar, geothermal, wave energy or wind power, the carbon footprint would be reduced considerably.
The use of NFTs opens the door to identifying new and capable artists while allowing the artists to gain value from their work. As more people get into NFTs, we expect to see huge players in fashion, design and art buying into the trading process.
Wakilisha Staff
Our mission is simple: to uplift and safeguard African culture, with all its diversity, for generations to come. We celebrate our heritage and ensure its enduring legacy through in-depth coverage of the happenings across the continent, engaging initiatives, and collaboration with other African cultural practitioners.